The JSON data type stores data in JSON objects. The JSON objects are top-level JSON objects comprising key-value pairs. In PostgreSQL, we can separately get the key and values for a JSON object using the two JSON functions; The json_each() function and the json_each_text() function. This blog primarily focuses on the json_each_text() function. So let’s learn about it.
PostgreSQL json_each_text() Function
The json_each_text() function works the same as the json_each() function does. It converts the JSON object into wide pairs/sets of keys and values. The difference between the json_each() function and the json_each_text() function comes in the return data type. The json_each() function gives the key in TEXT and the value in JSON format. while the json_each_text() function returns both the key and value in TEXT format.
The basic syntax for the json_each_text() function can be written as:
json_each_text(obj JSON) -> set_of RECORD(key TEXT, value TEXT)
In the above syntax:
● The Json_each_text() function takes in the JSON object as a parameter.
● The Json_each_text() function returns the set of expanded key-value pairs for that JSON object.
● The keys/values are collectively stored as RECORD.
● The returned Type of the “key” and “value” is the TEXT.
● The two separate columns for “key” and “value” can be returned as an output containing all the expanded key-value pairs in the respective top-level JSON object.
Let’s see how the PostgreSQL json_each_text() function can be implemented, using examples.
Example 1: Understanding the json_each_text() Function
Let’s consider the following query as an example of the json_each_text() function.
SELECT json_each_text(
'{"s_name": "Alex",
"s_id": 47,
"Courses_taken": ["applied Physics", "French", "Algebra"]}');We have passed the JSON object into the json_each_text() function. The function will be the key and values for the provided JSON object like this:
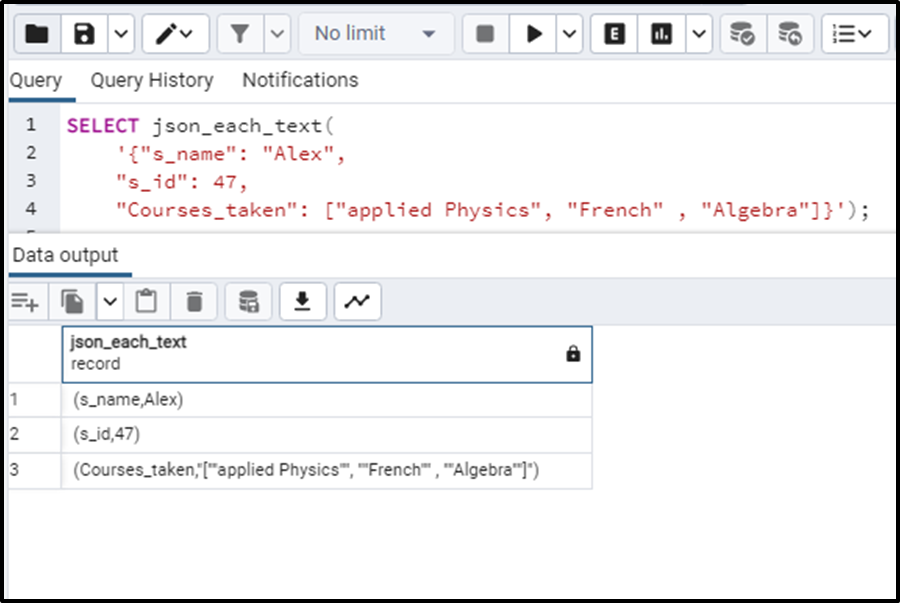
We can note that the function has given us the key-value pairs of the provided JSON object in an expanded form.
We can also get the keys and values in two different columns of a Postgres table.
Example 2: Using the json_each_text() Function
We can get the keys and values of a JSON object in two separate columns using the json_each_text() function. The same above example is considered here as well, to write the query for this scenario. The query looks like this:
SELECT * FROM json_each_text(
'{"s_name": "Alex",
"s_id": 47,
"Courses_taken": ["applied Physics", "French", "Algebra"]}');The query will return the keys and values in two separate columns of data like this:
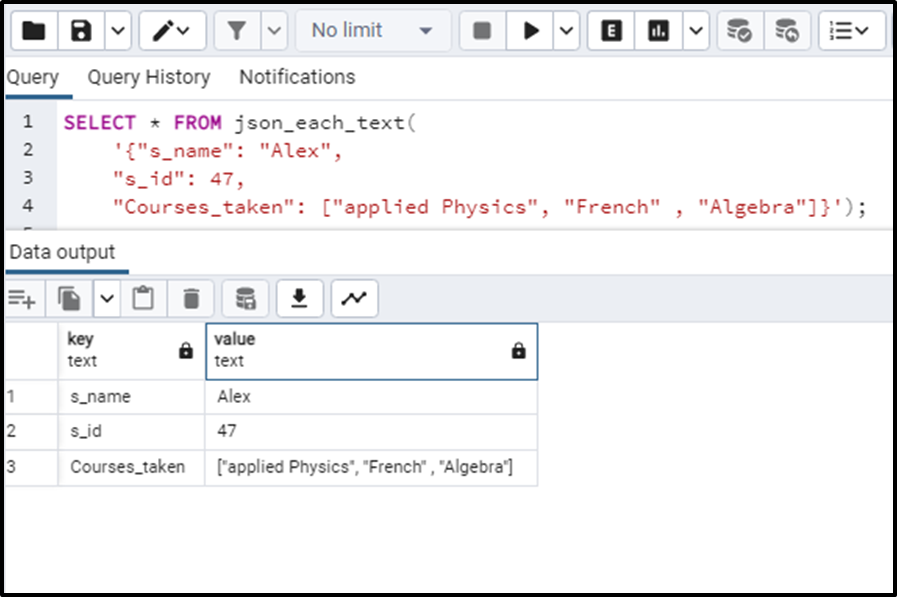
We can notice that the data type of both columns is TEXT. This is the point where the json_each_text() function is different from the json_each() function in Postgres.
In this way, the keys and values can be separated into 2 columns of a table. We can also custom-name these columns. For that, the query can be written like this:
SELECT * FROM json_each_text(
'{"s_name": "Alex",
"s_id": 47,
"Courses_taken": ["applied Physics", "French", "Algebra"]}')
AS col_names(new_key, new_val );We are customizing the new names for the key and value columns. The new titles are “new_key” for the “key” column and “new_val” for the “value” column. The output looks like this:
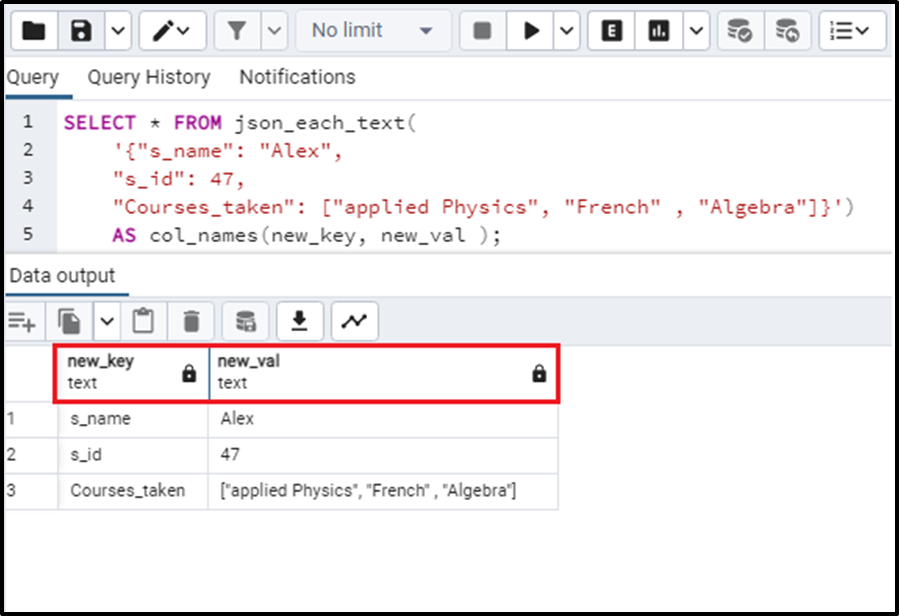
We can observe the new names instead of the old ones in the output.
Example 3: Using the json_each_text() Function on Table’s Data
We can use the json_each_text() function on a table “online_store” having a JSON object column. The table looks like this:
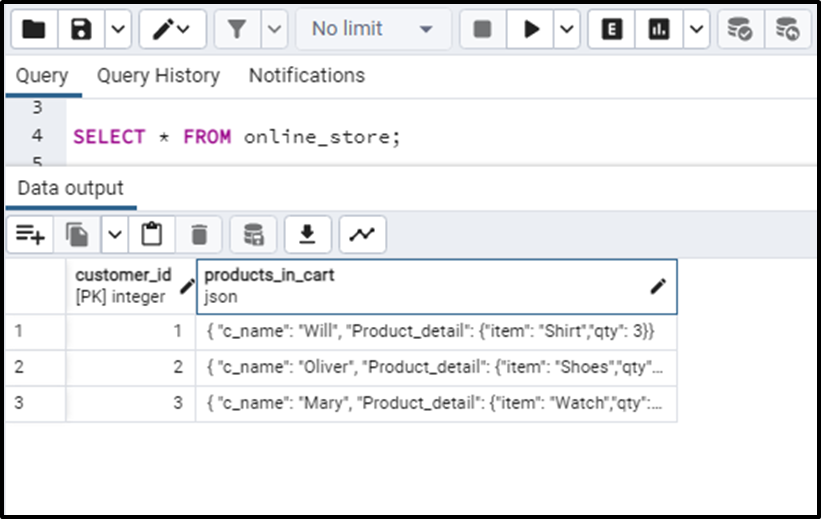
Now we will implement the json_each_text() function on the JSON column. We can write the following query:
SELECT json_each(products_in_cart) FROM online_store;
The query returns the keys and values as RECORDs for the table column.
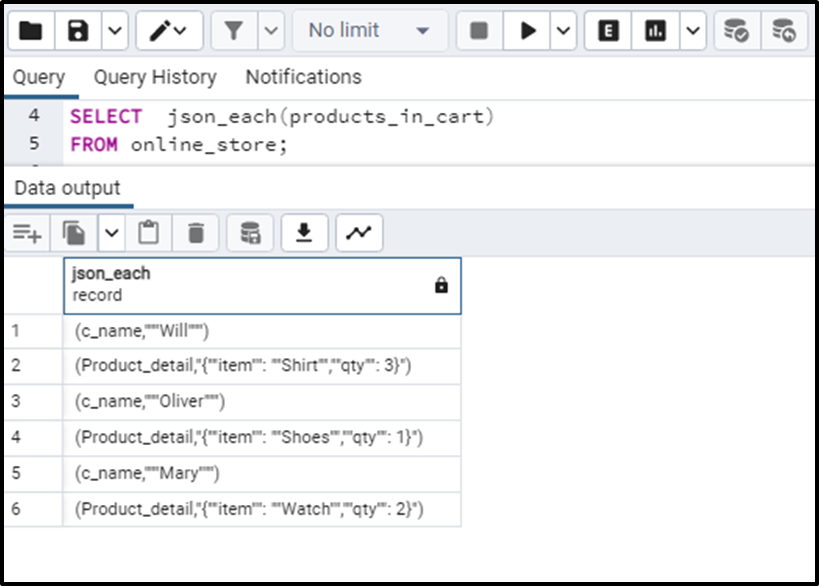
Now if we want to separate columns for keys and values, we will execute the following query:
SELECT * FROM online_store, json_each_text(products_in_cart);
This query will give the keys and values in separate columns.
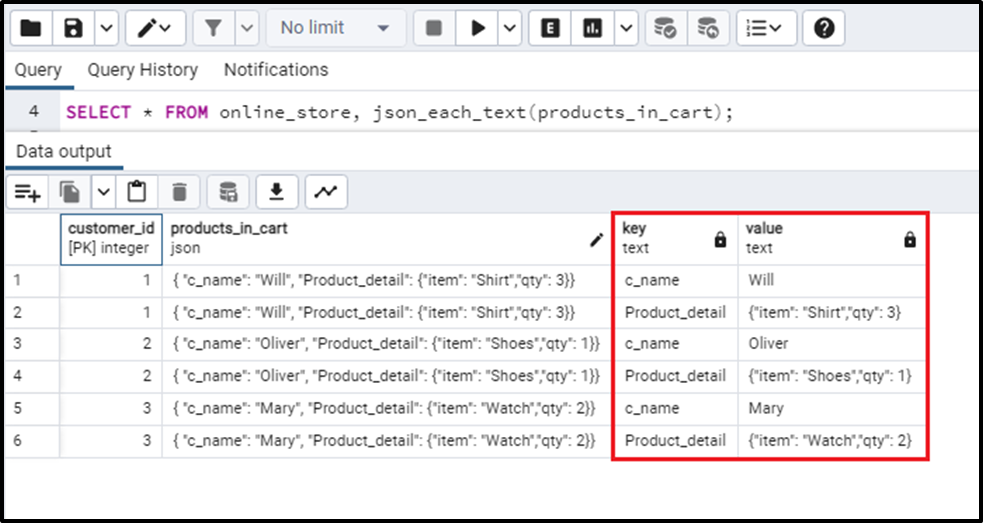
We can observe that the json_each_text() function has returned the values in the TEXT data type. This is how we can use the json_each_text() function with table data.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL json_each_text() function converts the JSON object into its small decomposed key-value pairs. The data type of keys and values is TEXT, this is the point where the json_each_text() function is different from the json_each() function. This tutorial comprised the details about the json_each_text() function and demonstrated how it is different from the json_each() function along with the proper examples.



